The purpose of this feature is to give scout leaders, educators and naturalists an idea of some of the natural events coming up each month. We will try to cover a variety of natural events ranging from sky events to calling periods of amphibians, bird and mammal watching tips, prominent wildflowers and anything else that comes to mind. We will also note prominent constellations appearing over the eastern horizon at mid-evening each month for our area for those who would like to learn the constellations. If you have suggestions for other types of natural information you would like to see added to this calendar, let us know! Note: You can click on the hyperlinks to learn more about some of the featured items. To return to the Calendar, hit the "back" button on your browser, NOT the "back" button on the web page. All charts are available in a "printer friendly" mode, with black stars on a white background. Left clicking on each chart will take you to a printable black and white image. Notes and Images From January 2006
We photographed these fossils being slowly encroached upon by mosses and lichens at the Wilderness Station at Barfield City Park in Murfreesboro, Tennessee. Evidence of ancient life can be found on much of the exposed limestone that borders the walking trails in the park.
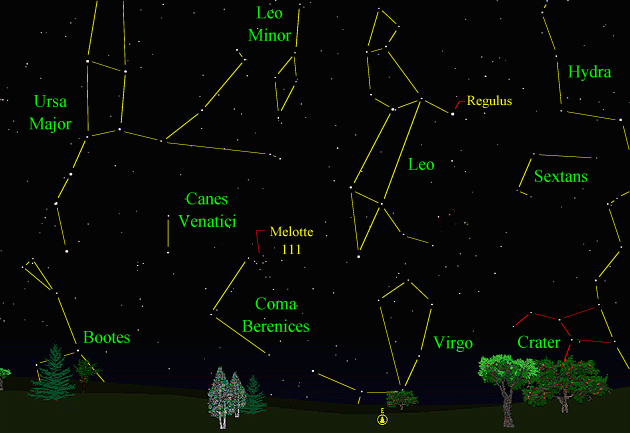
Sky Events for February 2006: Evening Sky: Saturn rules the evening sky, and at dusk is about 30 degrees above the eastern horizon at midmonth. Look for it below the bright stars Castor and Pollux in Gemini. This is a great time to view this magnificent planet and most small telescopes will deliver a stunning view. Mars continues to fade in the western sky. Look for it near the Pleiades in Taurus. Jupiter clears the eastern horizon just before midnight on the 15th. From the 15th of the month onward, watch low in the western sky about 40 minutes after sundown for Mercury. The fleet-footed messenger makes its most favorable evening appearance of the year this month. It reaches greatest elongation from the sun on February 23rd. A relatively flat western horizon will improve your view. Morning Sky: At the beginning of the month, Venus rises around 4:40am and will be bright and beautiful in the dawn sky. All times noted in the Sky Events are for Franklin, Tennessee and are Central Standard Time. These times should be pretty close anywhere in the mid-state area. Constellations: The views below show the sky looking east at 9:00pm CST on February 15th. The first view shows the sky with the constellation outlines and names depicted. Star and planet names are in yellow. Constellation names are in green. The second view shows the same scene without labels. Leo, the Lion, is prominent with its bright star Regulus. Use Regulus to guide you to the faint constellation of Sextans, the Sextant. Conspicuous in the northeast is Ursa Major, the Great Bear. The constellations of Bootes, the Herdsman, Coma Berenices, Berenice's Hair, Virgo, the Virgin and Crater, the Cup are all just making their way above the horizon and will be seen better next month. If you can't wait, you can always stay up a little later and watch them rise.
On Learning the Constellations: We advise learning a few constellations each month, and then following them through the seasons. Once you associate a particular constellation coming over the eastern horizon at a certain time of year, you may start thinking about it like an old friend, looking forward to its arrival each season. The stars in the evening scene above, for instance, will always be in the same place relative to the horizon at the same time and date each February. Of course, the planets do move slowly through the constellations, but with practice you will learn to identify them from their appearance. In particular, learn the brightest stars (like Regulus in the above scene looking east), for they will guide you to the fainter stars. Once you can locate the more prominent constellations, you can "branch out" to other constellations around them. It may take you a little while to get a sense of scale, to translate what you see on the computer screen or what you see on the page of a book to what you see in the sky. Look for patterns, like the stars of the "Big Dipper." The earth's rotation causes the constellations to appear to move across the sky just as the sun and the moon appear to do. If you go outside earlier than the time shown on the charts, the constellations will be lower to the eastern horizon. If you observe later, they will have climbed higher. As each season progresses, the earth's motion around the sun causes the constellations to appear a little farther towards the west each night for any given time of night. If you want to see where the constellations in the above figures will be on March 16th at 9:00pm CST, you can stay up till 11:00pm CST on the February 16th and get a preview. The westward motion of the constellations is equivalent to two hours per month. For instance, if you want to see what stars will be on your eastern horizon on May 16th at 9:00pm CST (3 months from now), you would need to get up at 3:00am CST on February 16th (3 months times 2 hours/month = 6 hours).
A good book to learn the constellations is H. A. Rey's
classic, The Stars, A New Way to See Them. Rey's depictions of the
constellations and witty commentary are terrific. A good general reference book on astronomy is the Peterson
Field Guide, A Field Guide to the Stars and Planets, by Pasachoff.
The book retails for around $14.00. A good beginners software program for learning the night sky is the Starry Night Beginner program. Visit the Starry Night web site at www.starrynight.com The program retails for around $30.00 and contains a wealth of information. Circumzenithal Arcs: Fall, Winter and Spring are good times to watch for these beautiful arcs that form directly overhead. Be sure to look upward in the late afternoon anytime you have wispy cirrus clouds in sky.
Amphibians:
The amphibian season continues to build in February. One trick to finding amphibians in winter is to go out on mild (50 degrees Fahrenheit or warmer) rainy nights. For safety, it is important that you have another person with you to help watch for traffic as you slowly drive the back roads. Look for things that cross the road in front of you and stop frequently and listen. Early breeding frogs like Southeastern Chorus Frogs, Spring Peepers and Wood Frogs are already calling by the first of the month. Spotted Salamanders and Tiger Salamanders also breed in January and February, and the eggs of both can often be found this time of year. Southern Leopard Frogs sometimes call on mild February nights. Towards the end of the month, given mild temperatures, you can sometimes hear American Toads beginning to call. In west Tennessee, Crawfish Frogs give their loud snoring calls starting in late February and continuing on into early March. At higher elevations, listen for Mountain Chorus Frogs towards the end of the month. Remember that on mild nights you may find frogs and toads out foraging that you do not hear until later in the season.
Birds: Many times when we have been out looking for amphibians in February we've witnessed courtship flights of the American Woodcock. Listen for the "peent" call at dusk and watch as the male Woodcock spirals upward till it's almost out of sight, then dives back to the ground, twisting and turning. For more about watching American Woodcocks see, "The Woodcock's Call." On February 2nd, 2003, we witnessed two Red-Shouldered Hawks mating in a wetland near Springfield, Tennessee. Be on the lookout for courtship displays of these and other hawks. Stick Nests: With the leaves down, this is a great time of year to find raptor stick nests. I make notes of all the nests I find and then periodically check them to see if anyone has "moved in." Many times Great Horned Owls make use of an old Red-Tailed Hawk's nest from the previous year. The owls can already be incubating eggs by the third week in January. Of the hawks, Arthur Cleveland Bent, in his "Life Histories of North American Birds of Prey," writes, "[Red-tailed Hawks]...begin their nest building late in February or early in March; I have seen a wholly new nest half completed and decorated with green pine twigs and down as early as February 18th, over a month before the eggs are laid...Typical nests are from 28 to 30 inches in outside diameter, the inner cavity being 14 or 15 inches wide and 4 or 5 inches deep...The nests are well made of sticks and twigs, half an inch or less in thickness, and neatly lined with strips of inner bark, of cedar, grapevine or chestnut, usnea, and usually at least a few green sprigs of pine, cedar or hemlock. Some nests are profusely and beautifully lined with fresh green sprigs of white pine, which are frequently renewed during incubation and during the earlier stages of growth of the young...They "stake out their claim" late in February or early in March...by marking the nest they propose to use with a sprig of green pine...I believe that the birds prefer to build a new nest each year, but they sometimes use the same nest for consecutive years..." Bent was writing about the Red-Tail Hawks in New England, so our times could be a little earlier.
You probably have already put out your bird feeders, but if you havenít you're missing out on a lot of good looks at winter feeder birds. This is a great time of year to start learning your birds. Watch and listen for winter residents such as White-throated and White-crowned Sparrows, Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers, Red-breasted Nuthatches, Golden-crowned Kinglets and Brown Creepers.
Recommended: Bird Finding in Tennessee, Michael Lee Bierly. A classic guide to finding birds in Tennessee. The Sibley Guide to Birds, David Allen Sibley The Sibley Guide to Birds of Eastern North America, David Allen Sibley This new Sibley Guide covers only eastern North America, is quite compact, and is less expensive than the larger Sibley. An inexpensive guide for beginners is the Golden Guide for Birds.
Wildflowers: One of the nice things about taking hikes in February is looking for early spring wildflowers like Spring Beauties, Harbinger-of-Spring and Cut-leaved Toothwort.
Archives (Remember to use the back button on your browser, NOT the back button on the web page!)
Natural Calendar
December 2005
Natural Calendar
November 2005
Natural Calendar
September 2005
Natural Calendar
February 2005
Natural Calendar
December 2004
Natural Calendar
November 2004
Natural Calendar
September 2004
Natural Calendar
February 2004
Natural Calendar
December 2003
Natural Calendar
November 2003
Natural Calendar
September 2003 Natural Calendar February 2003 Natural Calendar December 2002 Natural Calendar November 2002 Nature Notes Archives: Nature Notes was a page we published in 2001 and 2002 containing our observations about everything from the northern lights display of November 2001 to frog and salamander egg masses. Night scenes prepared with Starry Night Pro software All images and recordings © 2006 Leaps
|