The purpose of this feature is to give scout leaders, educators and naturalists an idea of some of the natural events coming up each month. We will try to cover a variety of natural events ranging from sky events to calling periods of amphibians, bird and mammal watching tips, prominent wildflowers and anything else that comes to mind. We will also note prominent constellations appearing over the eastern horizon at mid-evening each month for our area for those who would like to learn the constellations. If you have suggestions for other types of natural information you would like to see added to this calendar, let us know! Note: You can click on the hyperlinks to learn more about some of the featured items. To return to the Calendar, hit the "back" button on your browser, NOT the "back" button on the web page. All charts are available in a "printer friendly" mode, with black stars on a white background. Left clicking on each chart will take you to a printable black and white image. Though we link book references to nationwide sources, we encourage you to support your local book store whenever possible.
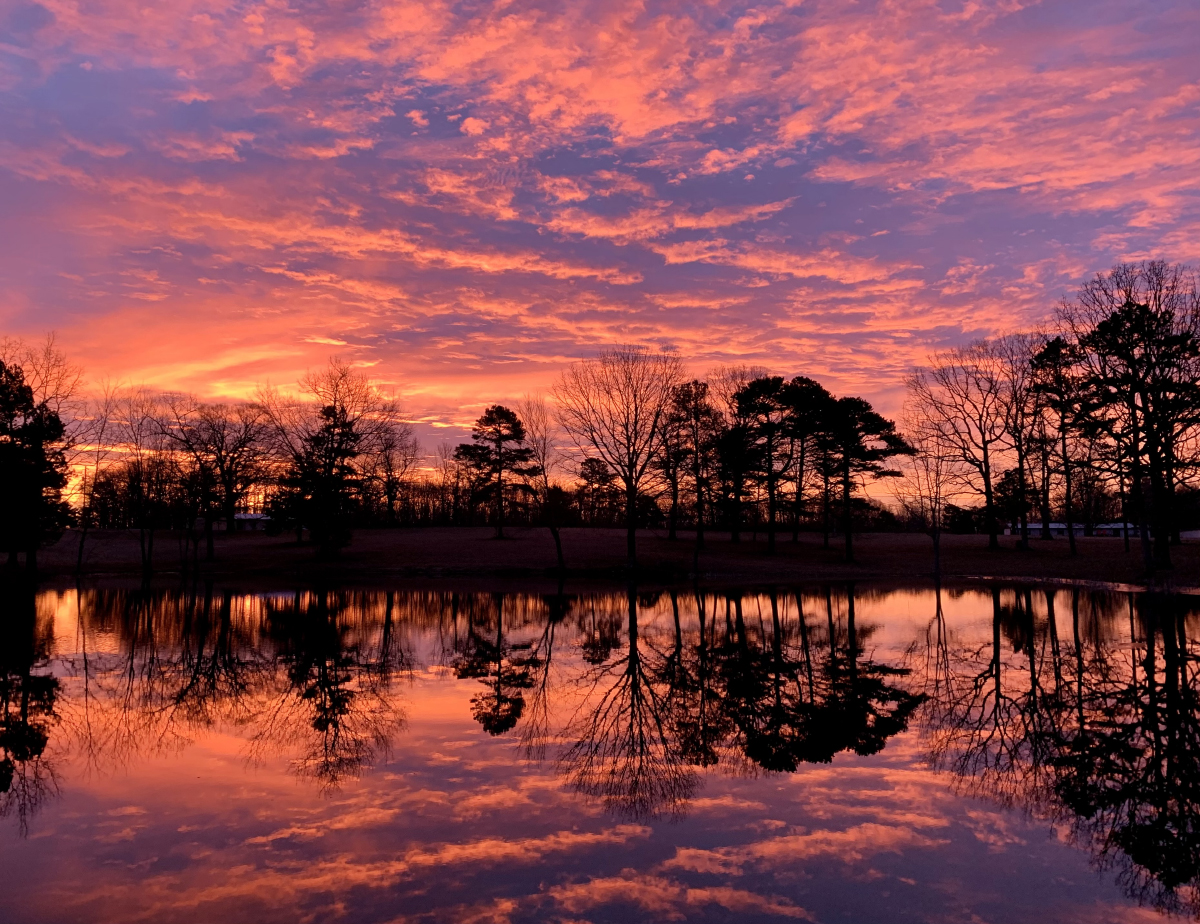
Notes From February 2021 I was treated to this colorful sunrise on February 4th. I noticed the intense colors and hurried out to the pond to catch this scene just a few minutes before the Sun appeared. Thirty minutes later the clouds thickened and the sky was overcast.
Daylight Savings Time begins on Sunday, March 14th at 2:00a.m. The March Equinox , signaling the beginning of spring in the Northern Hemisphere, is on March 20th at 5:37a.m. Eastern Daylight Time.Morning Sky:
Saturn will appear above and to the right of the pair, about 8-1/2 degrees away. In good quality binoculars you can see the oval shape of Saturn's rings (although the planet and rings blend together) and tell their orientation to the horizon. To spot the rings with binoculars you may want to steady your arms against an object like the top of your car. Use a star to adjust the individual focus of your binocular eyepieces so that both eyes see sharp focus at exactly the same focus position. Finally, you'll be able to see the oval shape of the rings better with increasing sky brightness. Try to determine the orientation of the rings relative to the horizon and then use an app like Sky Safari (see below) to see if you were right. All three planets are in Capricornus, the Sea Goat, certainly one of the stranger mythological creatures. Plan to be in a place that has a fairly flat eastern horizon about 30 minutes before sunrise. Mercury reaches its greatest elongation from the Sun the following day. On March 9th the waning crescent Moon will join the three planets. Again, try to be in place 30 minutes before sunrise. If you haven't paid much attention to the movement of the planets in the sky you will probably be amazed to see how different the grouping of the three planets appears just four days later!
Evening Sky: Mars drifts by the Pleiades this month and should be a pretty view in binoculars or in a small telescope. Telescopically, Mars appears tiny, only about 6 seconds of an arc in diameter. Mars will be within 5 degrees of the Pleiades from February 25th till March 11th. Constellations:
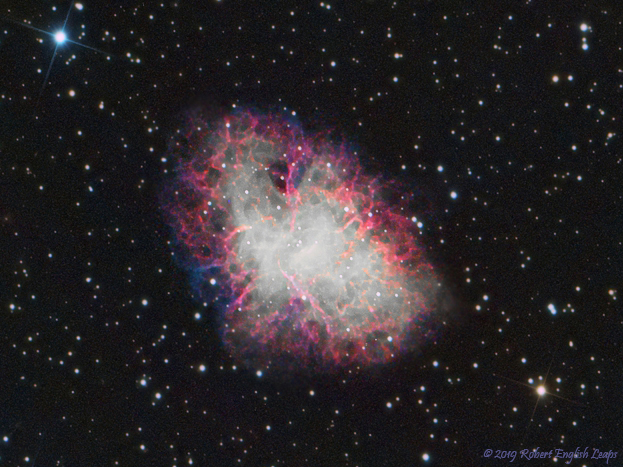
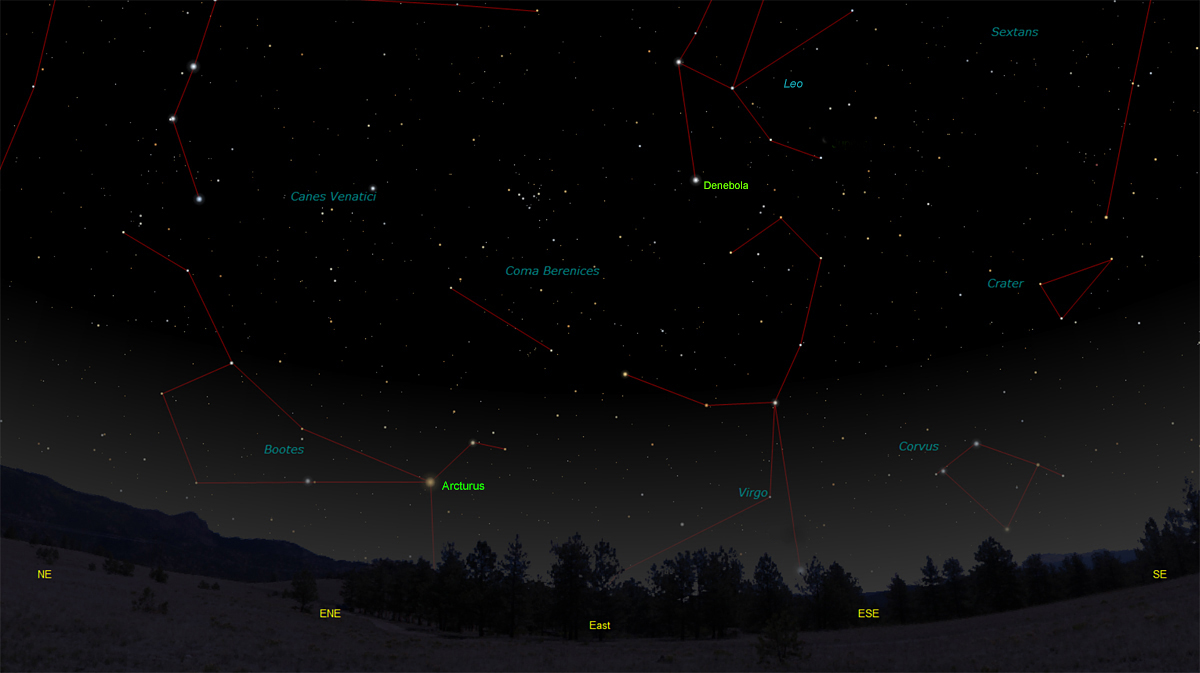
The bright star Arcturus, in Bootes, the Herdsman, makes its appearance this month in the early evening sky, a sure sign that Spring is here. Virgo clears the horizon this month along with Corvus, the Crow. The area of sky encompassing Leo, Virgo and Como Berenices marks the heart of the great Virgo cluster of galaxies. In the early morning hours Virgo will have risen high enough in the sky to search for the many bright galaxies that are in this region. Messier 104, in southern Virgo just above Corvus, is one of the easier galaxies to spot in binoculars. Even so, you will need a dark and moonless night to be successful. Messier 1, The Crab Nebula, is high in the sky this month and can sometimes be spotted in binoculars in a location away from city lights. In larger telescopes you can visually make out the part of the nebula that appears whitish in the above image. To me it looks to me like a giant rabbit grazing in some cosmic field of grass. The faint red and blue tendrils are visible only large telescopes in very dark skies. The Crab Nebula is the remnant of a stellar explosion that was noted by Chinese astronomers in the year 1054. The star collapsed to a rapidly spinning neutron star, and pulsar. It spins at a rate of 30 revolutions per second. Distance to the nebula is 6,500 light-years from Earth. For more on the crab nebula, including finder charts and a great interview with pulsar discoverer Jocelyn Bell Burnell, click here. The object is number one in 18th century French comet hunter Charles Messier's catalog of objects which might be confused with comets. In describing the appearance of the crab nebula, Messier said, "This nebula had such a resemblance to a comet, in its form and brightness, that I endeavored to find others, so that astronomers would not confuse these same nebulae with comets just beginning to shine." Messier ending up cataloging some of the most beautiful galaxies, nebulae and star clusters in the sky.
On Learning the Constellations: We advise learning a few constellations each month, and then following them through the seasons. Once you associate a particular constellation coming over the eastern horizon at a certain time of year, you may start thinking about it like an old friend, looking forward to its arrival each season. The stars in the evening scene above, for instance, will always be in the same place relative to the horizon at the same time and date each March. Of course, the planets do move slowly through the constellations, but with practice you will learn to identify them from their appearance. In particular, learn the brightest stars (Like Arcturus and Denebola in the above scene looking east), for they will guide you to the fainter stars. Once you can locate the more prominent constellations, you can "branch out" to other constellations around them. It may take you a little while to get a sense of scale, to translate what you see on the computer screen or what you see on the page of a book to what you see in the sky. Look for patterns, like the stars of Corvus the Crow. The earth's rotation causes the constellations to appear to move across the sky just as the sun and the moon appear to do. If you go outside earlier than the time shown on the charts, the constellations will be lower to the eastern horizon. If you observe later, they will have climbed higher. As each season progresses, the earth's motion around the sun causes the constellations to appear a little farther towards the west each night for any given time of night. The westward motion of the constellations is equivalent to two hours per month. Recommended: Sky & Telescope's Pocket Star Atlas is beautiful, compact star atlas. A good book to learn the constellations is Patterns in the Sky, by Hewitt-White. For sky watching tips, an inexpensive good guide is Secrets of Stargazing, by Becky Ramotowski.
A good general reference book on astronomy is the Peterson
Field Guide,
A Field Guide to the Stars and Planets, by Pasachoff. The book retails for around $14.00.
The Virtual Moon Atlas is a terrific way to learn the surface features of the Moon. And it's free software. You can download the Virtual Moon Atlas here. Apps: The Sky Safari 6 basic version is free and a great aid for the beginning stargazer. We really love the Sky Safari 6 Pro. Both are available for iOS and Android operating systems. There are three versions. The Pro is simply the best astronomy app we've ever seen. The description of the Pro version reads, "includes over 100 million stars, 3 million galaxies down to 18th magnitude, and 750,000 solar system objects; including every comet and asteroid ever discovered." A nother great app is the Photographer's Ephemeris. Great for finding sunrise, moonrise, sunset and moonset times and the precise place on the horizon that the event will occur. Invaluable not only for planning photographs, but also nice to plan an outing to watch the full moon rise. Available for both androids and iOS operating systems.
Amphibians:
Recommended: The Frogs and Toads of North America, Lang Elliott, Houghton Mifflin Co. Archives (Remember to use the back button on your browser, NOT the back button on the web page!) Natural Calendar February 2021 Natural Calendar December 2020 Natural Calendar November 2020 Natural Calendar September 2020 Natural Calendar February 2020 Natural Calendar December 2019 Natural Calendar November 2019 Natural Calendar September 2019 Natural Calendar February 2019 Natural Calendar December 2018 Natural Calendar November 2018 Natural Calendar September 2018 Natural Calendar February 2018 Natural Calendar December 2017 Natural Calendar November 2017 Natural Calendar October 2017Natural Calendar September 2017 Natural Calendar February 2017 Natural Calendar December 2016 Natural Calendar November 2016 Natural Calendar September 2016Natural Calendar February 2016 Natural Calendar December 2015 Natural Calendar November 2015 Natural Calendar September 2015 Natural Calendar November 2014 Natural Calendar September 2014 Natural Calendar September 2013 Natural Calendar December 2012 Natural Calendar November 2012 Natural Calendar September 2012 Natural Calendar February 2012 Natural Calendar December 2011 Natural Calendar November 2011 Natural Calendar September 2011 Natural Calendar December 2010 Natural Calendar November 2010 Natural Calendar September 2010 Natural Calendar February 2010 Natural Calendar December 2009 Natural Calendar November 2009 Natural Calendar September 2009 Natural Calendar February 2009 Natural Calendar December 2008 Natural Calendar November 2008 Natural Calendar September 2008 Natural Calendar February 2008 Natural Calendar December 2007 Natural Calendar November 2007 Natural Calendar September 2007 Natural Calendar February 2007 Natural Calendar December 2006 Natural Calendar November 2006 Natural Calendar September 2006 Natural Calendar February 2006
Natural Calendar December 2005
Natural Calendar November 2005
Natural Calendar September 2005
Natural Calendar February 2005
Natural Calendar December 2004
Natural Calendar November 2004
Natural Calendar September 2004
Natural Calendar February 2004
Natural Calendar December 2003
Natural Calendar November 2003 Natural Calendar February 2003 Natural Calendar December 2002 Natural Calendar November 2002 Nature Notes Archives: Nature Notes was a page we published in 2001 and 2002 containing our observations about everything from the northern lights display of November 2001 to frog and salamander egg masses. Night scenes prepared with The Sky Professional from Software Bisque All images and recordings © 2021 Leaps
|
|