The purpose of this feature is to give scout leaders, educators and naturalists an idea of some of the natural events coming up each month. We will try to cover a variety of natural events ranging from sky events to calling periods of amphibians, bird and mammal watching tips, prominent wildflowers and anything else that comes to mind. We will also note prominent constellations appearing over the eastern horizon at mid-evening each month for our area for those who would like to learn the constellations. If you have suggestions for other types of natural information you would like to see added to this calendar, let us know! Note: You can click on the hyperlinks to learn more about some of the featured items. To return to the Calendar, hit the "back" button on your browser, NOT the "back" button on the web page. All charts are available in a "printer friendly" mode, with black stars on a white background. Left clicking on each chart will take you to a printable black and white image. Notes and Images From November 2005
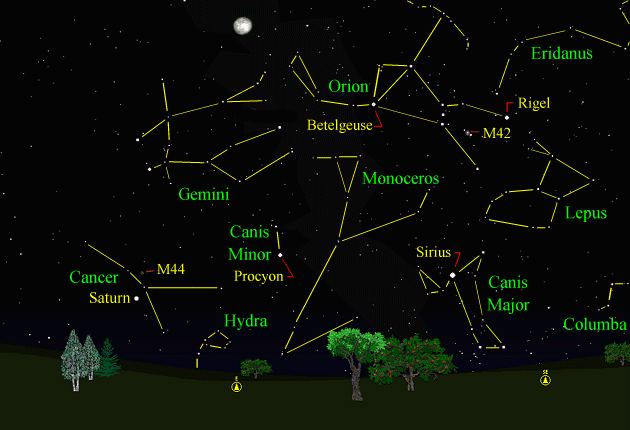
This male Cloudless Sulphur (Phoebis sennae) was photographed at Barfield Crescent Park in Murfreesboro on November 28th. Its bright attire looked out of place among the muted colors of the fall woods, like a bit of summer left behind. These butterflies are year-round residents in the Deep South, but extend their range northward during the spring and summer. Breeding colonies extend as far north as Canada. Larval host plants include partridge pea, wild senna, coffee senna and Christmas senna. In the fall, adults from the final generation begin the migration southward to the wintering grounds. Sky Events for December 2005: The Geminid Meteor Shower peaks on the evening of December 13th and the morning of December 14th. The waxing gibbous moon, one day before full, will reduce the number of meteors visible. The meteors will appear to radiate from the constellation of Gemini (see Constellations). The Winter Solstice: The winter solstice, corresponding with the shortest day of the year and the beginning of winter for the northern hemisphere, occurs at 12:35pm CST on December 21st. At this time, the northern hemisphere of the earth is tilted away from the sun the maximum amount possible. If these early sunsets are getting you down, you can take solace in the fact that the situation improves after December 5th. Because of the tilt of the earth’s axis relative to the plane of its orbit, the earliest sunset and the latest sunrise do not correspond with the shortest day of the year, which occurs on the 21st. The earliest sunset for our latitude occurs on December 5th, a little over two weeks before the solstice. The latest sunrise occurs on January 6th, a little over two weeks after the solstice. Evening Sky: Venus is dazzling in the western sky after sunset, appearing before any other star-like object. On December 4th, it pairs up with the crescent moon in the western sky after sunset. It reaches its peak brightness on December 9th. In any small telescope, or even in binoculars, it puts on quite a show. As it swings between the earth and the sun, it approaches the earth more closely than any other planet, and its apparent size grows from 36 seconds of an arc on the 1st to almost a minute of an arc on New Year's Eve. It appears as a 31-percent illuminated crescent on the 1st and thins to a spectacular very thin 5-percent illuminated crescent on the 31st. The crescent phase is visible even in binoculars, and is best viewed in the daytime against a blue sky (for tips on how to do this, and how to spot Venus with the naked eye in the daytime, see "Finding Venus by Day." To see the crescent Venus this way, perhaps with a few clouds drifting by in the foreground, is truly memorable. Mars is fading now after its close approach last month, and can be found due south around 8:30pm at mid-month. Saturn rises about 8:00pm in Cancer (see the star chart below). Morning Sky: Jupiter rises around 3:20am in Libra at mid-month. Mercury can be seen well in the dawn sky this month, and it reaches its greatest elongation from the sun on December 12th. Look for it in the southeast about 30-45 minutes before sunrise below Jupiter. All times noted in the Sky Events are for Franklin, Tennessee and are Central Standard Time. These times should be pretty close anywhere in the mid-state area. Constellations: The views below show the sky looking east at 9:00pm CST on December 15th. The first view has the constellation outlines and names depicted. Star and planet names are in yellow. Constellation names are in green. The second view shows the same view without labels. Saturn shines bright among the stars of Cancer, the Crab, and the bright star Sirius sparkles like a diamond below mighty Orion, the Hunter. Sirius is in Canis Major, the Great Dog, and is the brightest star in the night sky. It is known as the Dog Star. In the late summer, Sirius rises at the same time as the sun. Because of this, the late summer days are known as “the dog days." Compare the bright stars Betelgeuse and Rigel in Orion. Betelgeuse is a red giant and the star Rigel is a very hot, very bright supergiant. Compare the color of the two stars. If you have a telescope, point it to the center of the three "sword" stars below Orion's belt. You will be pointing at the Orion Nebula, M42, one of the most magnificent emission nebulas in the sky. It appears as a small greenish glow in small telescopes. Crouching beneath the feet of Orion, is Lepus, the hare. Below Lepus is Columba, the Dove. The faint constellation Monoceros, the Unicorn, follows Orion over the eastern horizon. Low in the eastern sky below Gemini is Canis Minor, with its bright star Procyon. Procyon means, "before the dog," and refers to the fact that Procyon rises just before the Dog Star, Sirus. Look below Gemini and see if you can spot the faint glow of M44, the "Beehive Cluster." This cluster is located in Cancer, the Crab. Finally, Hydra, the Water Serpent, rears its head just above the eastern horizon.
On Learning the Constellations: We advise learning a few constellations each month, and then following them through the seasons. Once you associate a particular constellation coming over the eastern horizon at a certain time of year, you may start thinking about it like an old friend, looking forward to its arrival each season. The stars in the evening scene above, for instance, will always be in the same place relative to the horizon at the same time and date each December. Of course, the planets do move slowly through the constellations, but with practice you will learn to identify them from their appearance. In particular, learn the brightest stars (like Sirius and Procyon in the above scene), for they will guide you to the fainter stars. Once you can locate the more prominent constellations, you can "branch out" to other constellations around them. It may take you a little while to get a sense of scale, to translate what you see on the computer screen or what you see on the page of a book to what you see in the sky. Look for patterns, like the three stars in a line in Orion's belt. The earth's rotation causes the constellations to appear to move across the sky just as the sun and the moon appear to do. If you go outside earlier than the time shown on the charts, the constellations will be lower to the eastern horizon. If you observe later, they will have climbed higher. As each season progresses, the earth's motion around the sun causes the constellations to appear a little farther towards the west each night for any given time of night. If you want to see where the constellations in the above figures will be on January 15th at 9:00pm CST, you can stay up till 11:00pm CST on the December 15th and get a preview. The westward motion of the constellations is equivalent to two hours per month. For instance, if you want to see what stars will be on your eastern horizon on March 15th at 9:00pm CST (3 months later), you would need to get up at 3:00am CST in the morning on December 15th (3 months times 2 hours/month = 6 hours). A good book to learn the constellations is H. A. Rey's
classic, The Stars, A New Way to See Them. Rey's depictions of the
constellations and witty commentary are terrific. A good general reference book on astronomy is the Peterson
Field Guide, A Field Guide to the Stars and Planets, by Pasachoff.
The book retails for around $14.00. A good beginners software program for learning the night sky
is the Starry Night Beginner program. Visit the Starry Night web site at
www.starrynight.com The program retails for around $30.00 and
contains a wealth of information.
Amphibians:
December really marks the beginning of the breeding season for our Tennessee frogs and toads. We have had breeding choruses of Southeastern Chorus Frogs as early as December 4th. Breeding even before Wood Frogs, these irrepressible inhabitants of flooded winter fields and other wet areas will call throughout the cold winter months. Listen for their call, which sounds like someone dragging their thumb across the teeth of a plastic comb, on mild wet winter evenings. Listen also for Southern Leopard Frogs. We hear them throughout the fall. Many other Tennessee frogs and toads can also be seen on mild December nights, but most are silent.
Birds: If you walk grassy fields that have some wetter areas, you may flush a Short-Eared Owl, a winter resident in Tennessee. We have flushed them from fields at Pardue’s Pond near Ashland City, along the roads that go to Pace Point near Big Sandy, Tennessee, at Britton Ford near Dover, Tennessee and at Savannah Bottoms, south of Savannah, Tennessee. These birds tend to occupy the same habitat as Northern Harriers, so if you see Harriers over grassy fields, be on the lookout for the owls. They often begin flying in the late afternoon, coursing over the fields like a Harrier. It’s a good idea to check any “Northern Harrier” you see in the late afternoon to make sure it’s not a Short-eared Owl. Through the end of December, listen for the courtship dueting of Great Horned Owls at dusk and dawn. You probably have already put out your bird feeders, but if you haven’t you're missing out on a lot of good looks at winter feeder birds. This is a great time of year to start learning your birds. Watch and listen for winter residents such as White-throated and White-crowned Sparrows, Yellow-bellied Sapsuckers, Red-breasted Nuthatches, Golden-crowned Kinglets and Brown Creepers. Recommended: Bird Finding in Tennessee, Michael Lee Bierly. A classic guide to finding birds in Tennessee. The Sibley Guide to Birds, David Allen Sibley The Sibley Guide to Birds of Eastern North America, David Allen Sibley This new Sibley Guide covers only eastern North America, is quite compact, and is less expensive than the larger Sibley. An inexpensive guide for beginners is the Golden Guide for Birds.
Archives (Remember to use the back button on your browser, NOT the back button on the web page!)
Natural Calendar
November 2005
Natural Calendar
September 2005
Natural Calendar
February 2005
Natural Calendar
December 2004
Natural Calendar
November 2004
Natural Calendar
September 2004
Natural Calendar
February 2004
Natural Calendar
December 2003
Natural Calendar
November 2003
Natural Calendar
September 2003 Natural Calendar February 2003 Natural Calendar December 2002 Natural Calendar November 2002 Nature Notes Archives: Nature Notes was a page we published in 2001 and 2002 containing our observations about everything from the northern lights display of November 2001 to frog and salamander egg masses. Night scenes prepared with Starry Night Pro software All images and recordings © 2005 Leaps
|